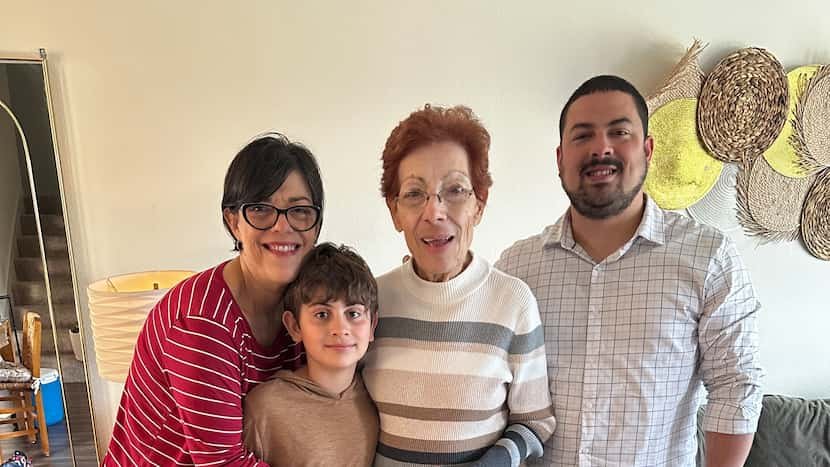
Janett Bell has watched her mother’s health decline since the 83-year-old woman was diagnosed with Alzheimer’s a year ago.
Janett’s mother, Carmen, began experiencing symptoms that many people consider normal for a person that age. Carmen lived alone in her house in Puerto Rico. Janett and her younger sister, Glorimar, who lives in Connecticut, visited their mom frequently.
On one of her visits to the island, Janett realized that her mother was starting to forget things she had done all her adult life, such as going to her monthly appointment to get her hair done.
Things got more serious when Carmen began to seclude herself at her home and stopped talking to her long-time neighbors.
The last straw that made Janett bring her mother to live in North Texas was when, on one of her visits to Puerto Rico, her sister found her mother in noticeable physical deterioration.
“She had lost a lot of weight, she had stopped eating,” said Bell, a Spanish teacher at Tarleton State University. She said her mother kept forgetting that she had food in the refrigerator.
“On one visit, my sister found in the refrigerator a pot full of spoiled rice with worms my mother had in there for who knows how long,” she said.
Living with Alzheimer’s
Alzheimer’s is a type of brain disease that is caused by damage to nerve cells (neurons) in the brain. The brain’s neurons are essential for thinking, walking, talking and all human activity.
Alzheimer’s is a type of dementia that causes problems with memory, thinking and behavior. Symptoms usually develop slowly and worsen over time until they are so severe that they interfere with daily tasks.
The brain changes of Alzheimer’s disease include the accumulation of the abnormal proteins beta-amyloid and phosphorylated tau, as well as the degeneration of neurons. The brain changes of Alzheimer’s disease are the most common contributor to dementia.
Eventually, the neuronal damage of Alzheimer’s extends to parts of the brain that enable essential bodily functions such as walking and swallowing.
Individuals become bed-bound and require around-the-clock care. Ultimately, Alzheimer’s disease is fatal.
Studies indicate that people age 65 and older survive an average of four to eight years after a diagnosis of Alzheimer’s dementia, yet some live as long as 20 additional years.
The most significant risk factors for late-onset Alzheimer’s are older age, genetics and having a family history of Alzheimer’s.
Five percent of people aged 65 to 74, 13.1% of people aged 75 to 84 and 33.3% of people aged 85 or older have Alzheimer’s dementia in the United States.
However, it is important to note that Alzheimer’s dementia is not a normal part of aging, and older age alone is not sufficient to cause Alzheimer’s dementia. Researchers have found many genes that increase the risk of Alzheimer’s. In fact, in 2022, researchers identified 31 new genes that appear to affect biological processes known to be at play in Alzheimer’s disease.
An estimated 6.7 million Americans of all ages are living with Alzheimer’s disease in 2023.
In 2020, approximately 400,000 Texans age 65 and older were living with Alzheimer’s, and over 1,079,000 family members and friends are providing care, according to the Dallas and Northeast Texas chapter of the Alzheimer’s Association.
Dallas County has an estimated 37,700 individuals over the age of 65 diagnosed with Alzheimer’s or other dementia, which is a 12.6% prevalence in the county.
Hispanics are more susceptible
Studies have revealed that the Latino population in the United States is 50% more likely to suffer from Alzheimer’s.
CDC estimated that by 2060, 3.5 million Hispanics will have Alzheimer’s.
Although the reasons why Latinos are more likely to suffer from Alzheimer’s are not fully known, neuropsychologist Imaris Rios-Vazquez said that food and a sedentary life are factors that contribute to developing Alzheimer’s among the Hispanic community.
“The type of food, not exercising and refusing to go see the doctor when the first symptoms appear, are factors that can cause Alzheimer’s to develop”, said Rios-Vazquez, who is a cognitive research manager and co-director of the neuropsychology clinic at the Kerwin Medical Center in Dallas.
Rios-Vazquez said there are things people can do to try to prevent the shadow of Alzheimer’s from haunting their lives.
“You have to do simple things like walking 20 or 30 minutes every day, everything that helps the heart helps the brain,” Rios-Vazquez said.
“Hispanics like to eat a lot of tamales, cakes and all those tasty things, but we must concentrate on eating vegetables, nuts, whole grain flours and fish, that helps to have a lower risk of developing dementia,” said Rios-Vazquez, who was born and raised in Puerto Rico.
Studies indicate that Hispanics also have a high risk of diabetes, which, among other chronic conditions, is associated with Alzheimer’s disease. Further adding complexity to the overall picture of Alzheimer’s disease among Hispanics is the racial and cultural diversity of the Hispanic population in the U.S.
Rios-Vazquez said that exercising the brain is another excellent tool that helps to put up barriers against Alzheimer’s.
“Doing new things for the brain helps a lot. At an older age, there are people who want to learn to play an instrument or a new language and that’s great because it helps the brain. Knowing and learning new situations greatly helps the brain’s plasticity,” Rios-Vazquez said.
Help is available
In Texas, approximately 1 million unpaid caregivers provided care to Texans with Alzheimer’s in 2022, which equates to an estimated 1.5 billion hours of unpaid care at a cost of approximately $23.6 billion per year.
Total annual payments for health care, long-term care and hospice care in the U.S. for individuals with Alzheimer’s and other dementias are projected to increase from approximately $345 billion in 2023 to nearly $1 trillion in 2050, according to the Alzheimer’s Association.
“Caring for a loved one who has Alzheimer’s is a great challenge for families,” said Terri Contreras, a bilingual caregiver support specialist.
Contreras, who works with The Senior Source, said the nonprofit organization helps families who have a loved one with Alzheimer’s find the resources to cope with the situation.
Contreras explained that programs that can offer help range from transporting patients to their medical appointments to contacting caregivers trained to care for people with Alzheimer’s.
“It’s overwhelming, but we can help people throughout that process,” said Contreras, who manages support groups in English and Spanish for families who care for people with Alzheimer’s or other types of dementia.
Emotional stress
The emotional toll on people who care for loved ones with Alzheimer’s is perhaps the highest price to pay.
“It’s hard to see those changes, it’s hard to accept that your loved one has this disease,” Bell said of her mother’s deteriorating health. “There are days when she doesn’t let herself be helped, she doesn’t want to take her medications. It’s a tough situation and emotionally and physically draining.”
Contreras knows that people who care for a loved one with Alzheimer’s also need emotional support.
“People get tired and need a break. They need someone to help them, someone to trust to leave their house for a while and live their life,” Contreras said.
Bell relies on her husband for support and also has the help of her sister, who takes her mom to her house in Connecticut for periods.
“My husband’s support has been crucial. My husband and I always go out to eat on Fridays, it’s our date”, Bell said. “Emotional therapy, going to church, reading and attending my support group has helped me a lot.”
Despite all the support she gets, there are times when Bell feels like she is carrying the world on her shoulders.
“I have always considered myself a loving and patient person, but at the same time, I feel like there are days when I can’t take it anymore and I keep repeating myself: ‘Why did this have to happen to her, why to my mom?’ ” Bell said. “I just want my mom back home. I want the mom I knew before she had Alzheimer’s.”
Helping resources
Alzheimer’s Association Dallas and Northeast Texas Chapter
24/7 Helpline: 800-272-3900
Location: 5000 Quorum Drive, Suite 530, Dallas
Kerwin Medical Center
Phone: 972-433-9100
Location: 8198 Walnut Hill Lane, Jackson Building, Suite 100, Dallas
The Senior Source
Phone: 214-823-5700
Location: 3910 Harry Hines Blvd., Dallas